これはインタラクティブなノートブックです。ローカルで実行するか、以下のリンクを使用できます:
PII データと共に Weave を使用する方法
このガイドでは、個人を特定できる情報(PII)データをプライベートに保ちながら、W&B Weave を使用する方法を学びます。このガイドでは、PII データを特定、編集、匿名化するための以下の方法を紹介します:- 正規表現 を使用して PII データを特定し、編集します。
- Microsoft の Presidio、Python ベースのデータ保護 SDK。このツールは編集と置換機能を提供します。
- Faker、偽のデータを生成するための Python ライブラリで、Presidio と組み合わせて PII データを匿名化します。
weave.op 入力/出力ロギングのカスタマイズ および autopatch_settings を使用して PII 編集と匿名化をワークフローに統合する方法を学びます。詳細については、ログに記録される入力と出力をカスタマイズするを参照してください。
始めるには、以下を行います:
- 概要 セクションを確認します。
- 前提条件を完了します。
- 利用可能な方法 を確認して、PII データを特定、編集、匿名化します。
- Weave 呼び出しに方法を適用する。
概要
以下のセクションでは、weave.op を使用した入力と出力のロギングの概要と、Weave で PII データを扱うためのベストプラクティスを提供します。
を使用して入力と出力のロギングをカスタマイズする weave.op
Weave Ops では、入力と出力の後処理関数を定義できます。これらの関数を使用して、LLM 呼び出しに渡されるデータや Weave にログ記録されるデータを変更できます。
次の例では、2つの後処理関数が定義され、weave.op()の引数として渡されます。
PII データで Weave を使用するためのベストプラクティス
PII データで Weave を使用する前に、PII データで Weave を使用するためのベストプラクティスを確認してください。テスト中
- PII 検出を確認するために匿名化されたデータをログに記録する
- Weave Traces で PII 処理プロセスを追跡する
- 実際の PII を公開せずに匿名化のパフォーマンスを測定する
本番環境で
- 生の PII を絶対にログに記録しない
- ログに記録する前に機密フィールドを暗号化する
暗号化のヒント
- 後で復号化する必要があるデータには可逆的な暗号化を使用する
- 元に戻す必要のない一意の ID には一方向ハッシュを適用する
- 暗号化されたまま分析する必要があるデータには特殊な暗号化を検討する
前提条件
- まず、必要なパッケージをインストールします。
- Weave プロジェクトを初期化します。
- デモ PII データセットをロードします。これには 10 個のテキストブロックが含まれています。
編集方法の概要
セットアップを完了したら、 PII データを検出して保護するために、以下の方法を使用して PII データを特定、編集し、オプションで匿名化します:- 正規表現 を使用して PII データを特定し、編集します。
- Microsoft Presidio、編集と置換機能を提供する Python ベースのデータ保護 SDK。
- Faker、偽のデータを生成するための Python ライブラリ。
方法 1:正規表現を使用したフィルタリング
正規表現(regex) は PII データを特定して編集する最も簡単な方法です。正規表現を使用すると、電話番号、メールアドレス、社会保障番号などの機密情報のさまざまな形式に一致するパターンを定義できます。正規表現を使用すると、より複雑な NLP 技術を必要とせずに、大量のテキストをスキャンして情報を置換または編集できます。方法 2:Microsoft Presidio を使用した編集
次の方法は、Microsoft Presidio を使用した PII データの完全な削除です。Presidio は PII を編集し、PII タイプを表すプレースホルダーに置き換えます。例えば、Presidio はAlex を "My name is Alex" 内の <PERSON> に置き換えます。
Presidio には 一般的なエンティティ のサポートが組み込まれています。以下の例では、PHONE_NUMBER、PERSON、LOCATION、EMAIL_ADDRESS または US_SSN であるすべてのエンティティを編集します。Presidio のプロセスは関数にカプセル化されています。
方法 3:Faker と Presidio を使用した置換による匿名化
テキストを編集する代わりに、MS Presidio を使用して名前や電話番号などの PII を Faker Python ライブラリを使用して生成された偽のデータと交換することで匿名化できます。例えば、次のようなデータがあるとします:"My name is Raphael and I like to fish. My phone number is 212-555-5555"
データが Presidio と Faker を使用して処理された後、次のようになる可能性があります:
"My name is Katherine Dixon and I like to fish. My phone number is 667.431.7379"
Presidio と Faker を効果的に一緒に使用するには、カスタムオペレーターへの参照を提供する必要があります。これらのオペレーターは、Presidio を PII を偽のデータと交換する責任を持つ Faker 関数に誘導します。
方法 4: を使用する autopatch_settings
を使用して、サポートされている LLM 統合の 1 つまたは複数の初期化中に直接 PII 処理を構成できます。この方法の利点は次のとおりです:autopatch_settings PII 処理ロジックは初期化時に一元化されスコープ化されるため、散在するカスタムロジックの必要性が減少します。
- PII 処理ワークフローは、特定の統合のためにカスタマイズしたり、完全に無効にしたりできます。
- PII 処理ワークフローは特定の統合のためにカスタマイズまたは完全に無効化できます。
autopatch_settings PII 処理を構成するには、postprocess_inputs および/または postprocess_output を op_settings 内のサポートされている LLM 統合のいずれかに定義します。
Weave 呼び出しに方法を適用する
以下の例では、PII 編集と匿名化の方法を Weave Models に統合し、結果を Weave Traces でプレビューします。 まず、Weave Model。Weave Modelは、モデルの動作を定義する構成設定、モデルの重み、コードなどの情報の組み合わせです。 私たちのモデルでは、Anthropic APIが呼び出される予測関数を含めます。Anthropicの Claude Sonnetは、Traces を使用してLLM呼び出しをトレースしながら感情分析を実行するために使用されますTraces。Claude Sonnetはテキストブロックを受け取り、以下の感情分類のいずれかを出力します:positive、negative、またはneutral。さらに、PIIデータがLLMに送信される前に編集または匿名化されるようにするための後処理関数も含めます。 このコードを実行すると、Weaveプロジェクトページへのリンクと、実行した特定のトレース(LLM呼び出し)へのリンクが表示されます。正規表現メソッド
最も単純なケースでは、正規表現を使用して元のテキストからPIIデータを特定し、編集することができます。Presidio編集メソッド
次に、Presidioを使用して元のテキストからPIIデータを特定し、編集します。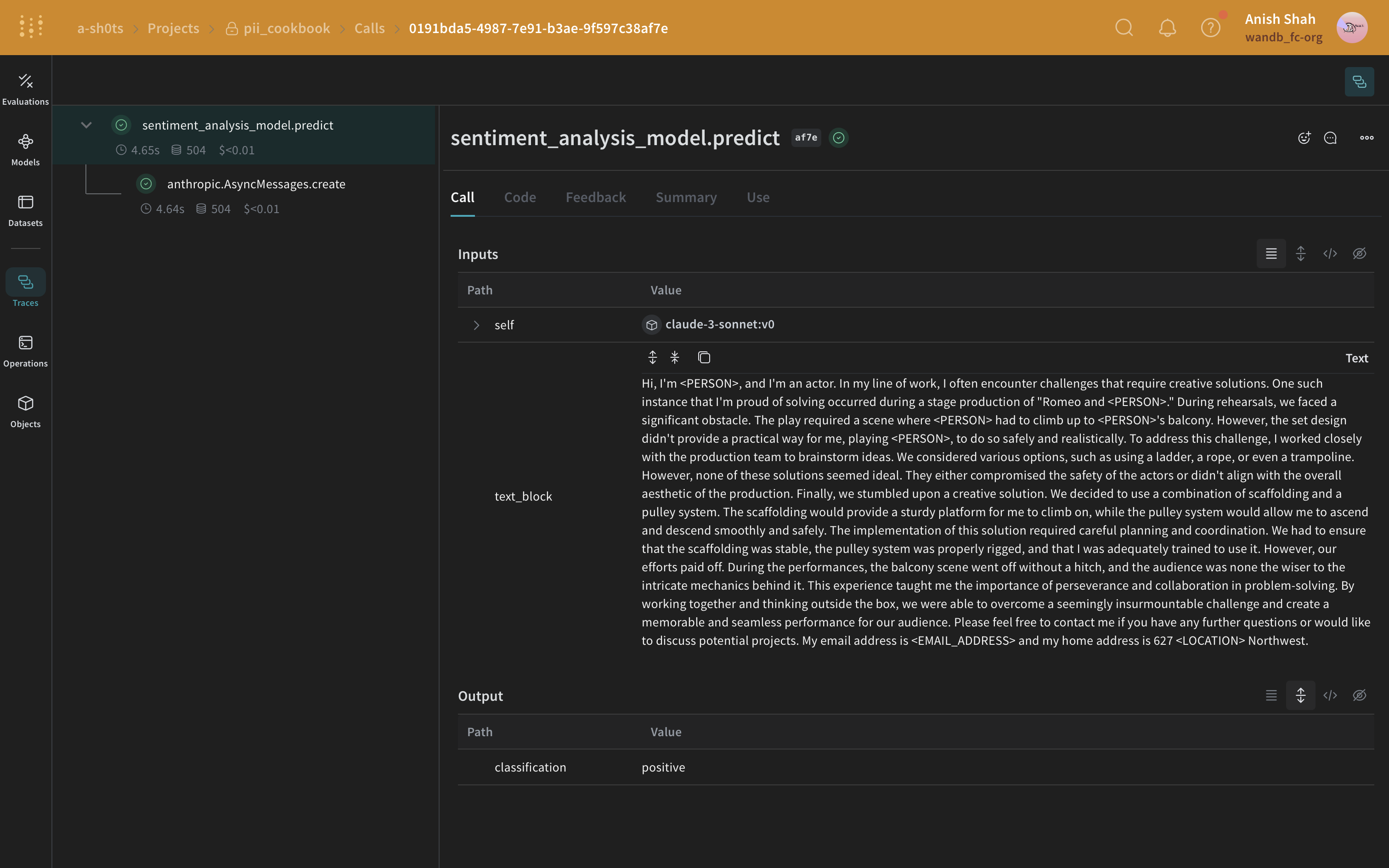
FakerとPresidio置換メソッド
この例では、Fakerを使用して匿名化された代替PIIデータを生成し、Presidioを使用して元のテキスト内のPIIデータを特定して置き換えます。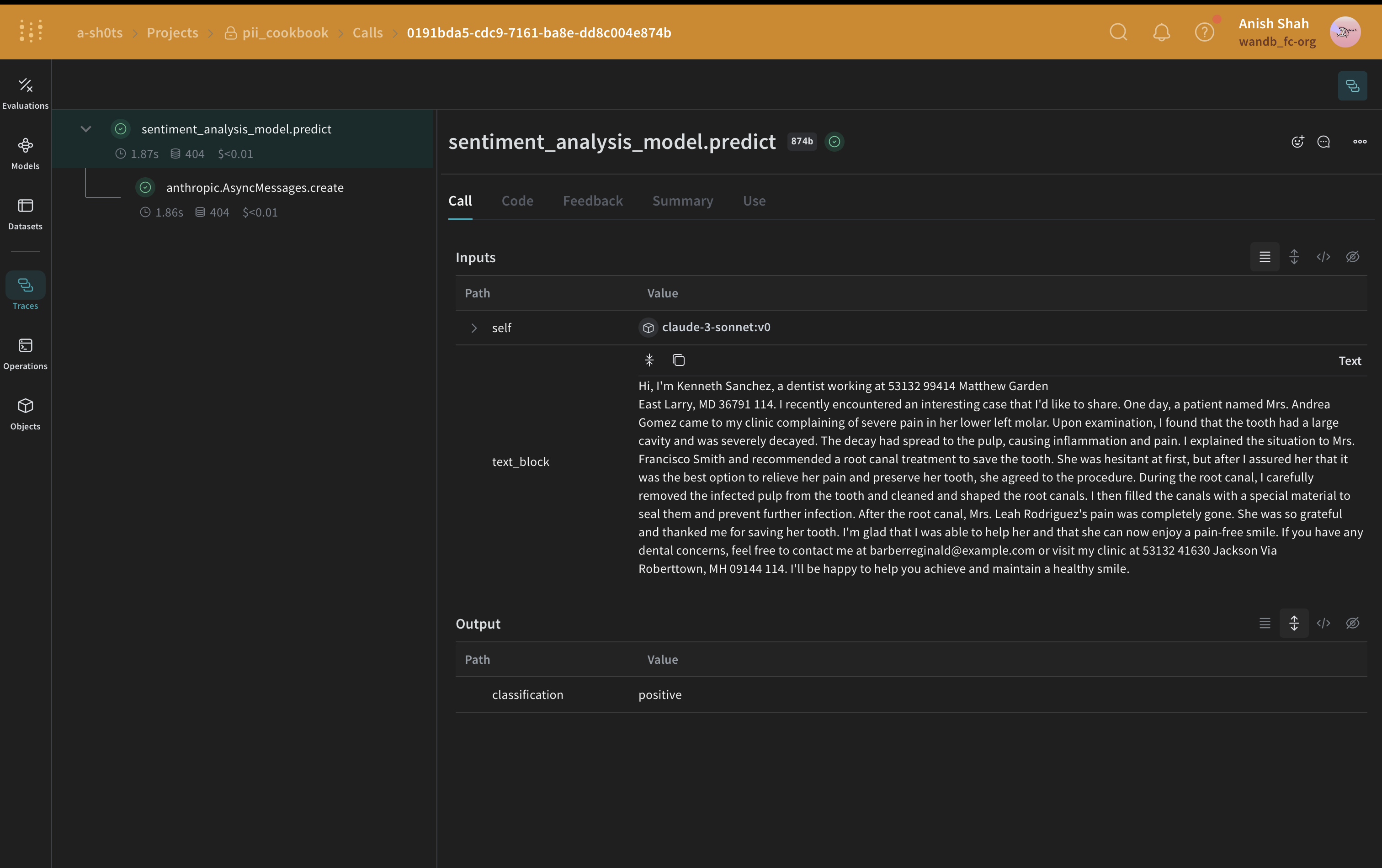
autopatch_settingsメソッド
次の例では、postprocess_inputsのanthropicをpostprocess_inputs_regex()関数()に初期化時に設定します。postprocess_inputs_regex関数はredact_with_regexで定義されているメソッド1:正規表現フィルタリングを適用します。これで、redact_with_regexはすべてのanthropicモデルへの入力に適用されます。
(オプション)データの暗号化
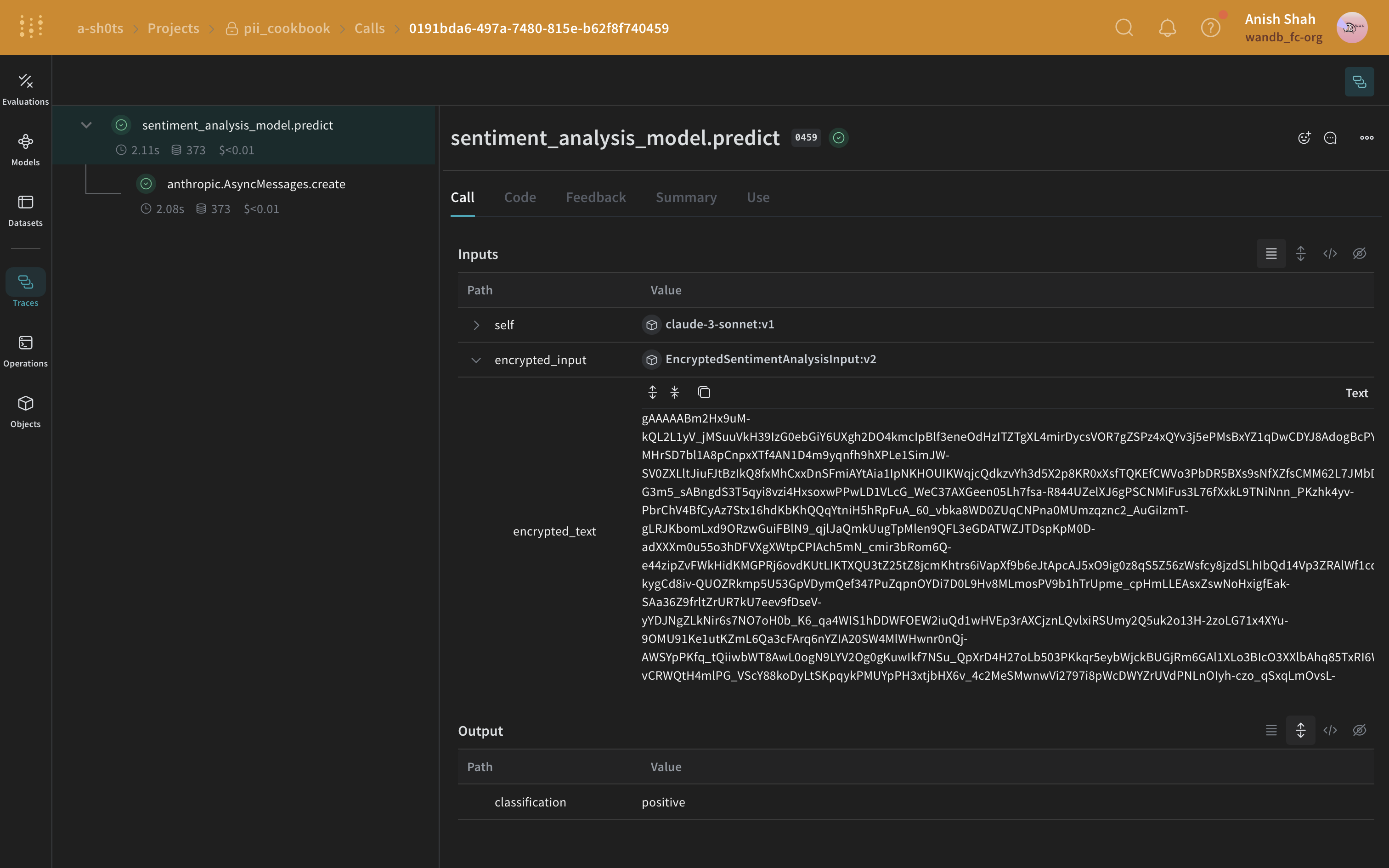 PIIの匿名化に加えて、cryptographyライブラリのFernet対称暗号化を使用してデータにセキュリティの追加層を加えることができます。このアプローチにより、匿名化されたデータが傍受されても、暗号化キーなしでは読み取れないことが保証されます。
PIIの匿名化に加えて、cryptographyライブラリのFernet対称暗号化を使用してデータにセキュリティの追加層を加えることができます。このアプローチにより、匿名化されたデータが傍受されても、暗号化キーなしでは読み取れないことが保証されます。

